Are you aware of what happens when you eat too much sugar? You might think a little extra sweetness is harmless, but the truth is, it can affect your body in surprising ways.
From sudden energy crashes to long-term health problems, too much sugar can take a serious toll on your well-being. If you want to protect your health and feel better every day, it’s important to understand these side effects now. Keep reading to discover how sugar might be impacting your body—and what you can do to stay in control.
Sugar And Your Body
Sugar gives quick energy, but too much can harm your body. It affects many parts inside you. Knowing how sugar works helps you make better choices. Your body reacts to sugar in ways that change health over time.
Eating a lot of sugar often leads to problems with weight, energy, and organs. Let’s explore how sugar affects your metabolism and blood sugar levels.
How Sugar Affects Metabolism
Metabolism is how your body turns food into energy. Sugar is a fast source of energy, but too much can slow this process. Your body may start storing extra sugar as fat. This can lead to weight gain and tiredness. Over time, your metabolism can become less efficient.
Eating large amounts of sugar regularly forces your body to work harder. This can cause insulin resistance, which lowers your body’s ability to use sugar properly. A slower metabolism means less energy and more health issues.
Impact On Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar is the amount of sugar in your blood. It gives energy to your cells. When you eat a lot of sugar, your blood sugar spikes quickly. This sudden rise can cause your body to release a lot of insulin.
High insulin levels can cause your blood sugar to drop fast, making you feel tired or hungry soon after. Over time, these spikes and drops can damage your blood vessels and organs. It also raises the risk of diabetes and heart disease.

Credit: continentalhospitals.com
Weight Gain And Obesity
Eating too much sugar can cause weight gain and lead to obesity. Sugar adds extra calories without filling you up. Over time, these extra calories turn into stored fat. This weight gain can increase the risk of many health problems.
Sugar’s Role In Fat Storage
Sugar, especially fructose, is processed by the liver. The liver converts excess sugar into fat. This fat then accumulates in the body. It often collects around the belly, which is linked to health risks. The body stores this fat for energy, but too much leads to obesity.
Link Between Sugar And Appetite
Sugar affects hormones that control hunger. It can reduce feelings of fullness after eating. This makes you want to eat more food. Drinking sugary drinks does not satisfy hunger well. This causes more calorie intake and weight gain.
Heart Health Dangers
Eating too much sugar can harm your heart in many ways. Sugar affects blood vessels and the way your heart works. It can cause serious problems over time. Understanding these dangers helps you make better food choices.
Increased Risk Of Heart Disease
High sugar intake raises the risk of heart disease. Sugar causes inflammation in the body. This inflammation damages blood vessels and the heart. It also leads to higher levels of bad cholesterol. These changes increase the chance of heart attacks and strokes.
Sugar And Blood Pressure
Sugar can raise your blood pressure. Too much sugar makes your body hold extra salt and water. This adds strain on the heart and blood vessels. High blood pressure forces the heart to work harder. Over time, this can lead to heart failure and other issues.
Diabetes And Insulin Resistance
Eating too much sugar can harm your body in many ways. One serious problem is diabetes and insulin resistance. These conditions affect how your body uses sugar for energy. Understanding these issues helps you protect your health.
How Excess Sugar Triggers Diabetes
When you eat too much sugar, your blood sugar levels rise quickly. Your pancreas works hard to produce insulin. Insulin helps move sugar from blood into cells for energy.
Over time, high sugar intake makes your body less sensitive to insulin. This means your cells do not respond well. Your pancreas then makes more insulin to compensate.
This extra demand strains the pancreas. It may fail to keep up with the insulin needs. Blood sugar stays high, leading to type 2 diabetes. Excess sugar is a key factor in this process.
Signs Of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance happens before diabetes. Your body needs more insulin to manage blood sugar.
Common signs include feeling tired often and increased hunger. You might also notice weight gain, especially around the belly. Dark patches of skin can appear on the neck or armpits.
High blood sugar may cause frequent urination and thirst. Spotting these signs early can help you seek medical advice. Managing sugar intake is crucial to reduce insulin resistance.
Dental Problems
Eating too much sugar causes serious dental problems. Sugar feeds harmful bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria produce acids that attack teeth. Over time, this acid breaks down tooth enamel. Enamel is the hard outer layer that protects teeth. Once enamel wears away, teeth become weak and sensitive. This damage leads to cavities and tooth decay. Poor dental health affects eating and speaking. It may cause pain and infections. Understanding how sugar harms teeth helps prevent these problems.
Sugar And Tooth Decay
Sugar acts as food for bacteria in your mouth. Bacteria use sugar to make acids. These acids attack tooth enamel every time you eat sugar. Frequent sugar intake means constant acid attacks. This weakens enamel and causes tiny holes called cavities. Cavities can grow deeper and reach the tooth’s inside. This causes pain and may need fillings or root canals. Soft drinks, candies, and desserts have high sugar. Avoiding or limiting these foods protects your teeth.
Preventing Cavities
Brush teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Fluoride helps rebuild and strengthen enamel. Floss daily to remove sugar and bacteria between teeth. Drink water after eating sugary foods to wash away sugar. Regular dental checkups catch problems early. Avoid snacking on sugary foods between meals. Choose fruits, vegetables, and cheese as snacks. These foods help keep your mouth healthy. Simple habits can stop cavities and keep your smile bright.
Effects On Mental Health
Eating too much sugar does more than affect your body. It also impacts your mind. High sugar intake can change how you feel and think. This can lead to problems with mental health. Understanding these effects helps you make better choices for your mood and brain.
Sugar And Mood Swings
Sugar causes quick energy bursts. These bursts are often followed by crashes. The crash can make you feel tired and irritable. This cycle creates mood swings. Your emotions can become hard to control. Over time, mood swings may worsen with constant sugar highs and lows.
Connection To Anxiety And Depression
Too much sugar links to higher anxiety levels. It can also increase the risk of depression. Sugar affects brain chemicals that control mood. It can cause inflammation in the brain. This inflammation may worsen feelings of anxiety and sadness. Reducing sugar intake can help stabilize your mood.
Skin Issues Linked To Sugar
Eating too much sugar affects more than just your waistline. It can harm your skin in many ways. The sugar you eat can cause skin problems. These issues make your skin look unhealthy and aged.
Sugar’s Role In Acne
Sugar spikes insulin levels in your body. This causes oil glands to produce more oil. Excess oil clogs pores and leads to acne. Sugar also increases inflammation. Inflamed skin worsens acne and slows healing. Cutting down sugar can reduce breakouts and improve skin clarity.
Premature Aging And Wrinkles
Sugar attaches to proteins in your skin. This process is called glycation. Glycation damages collagen and elastin fibers. These fibers keep your skin firm and elastic. Damaged fibers cause skin to sag and wrinkle early. High sugar intake speeds up this aging process. Eating less sugar helps maintain youthful skin longer.
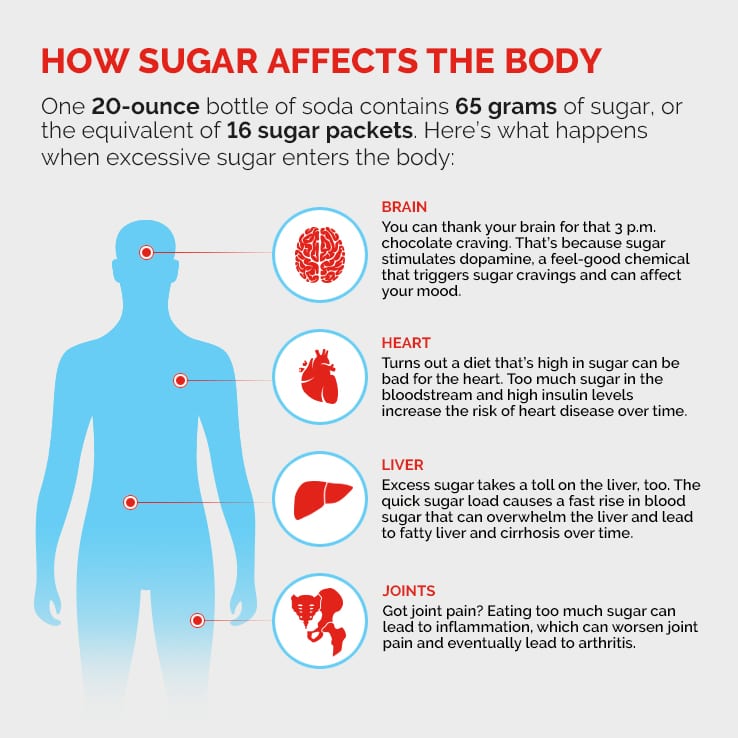
Credit: healthmatters.nyp.org
Digestive System Concerns
Eating too much sugar can cause problems in the digestive system. This affects how your body breaks down food and absorbs nutrients. It can also change the balance of bacteria in your gut. These changes might lead to discomfort and other health issues.
Gut Health And Sugar
Sugar feeds harmful bacteria in the gut. These bacteria grow faster and crowd out good bacteria. A poor balance can cause bloating, gas, and stomach pain. It also weakens the gut lining, making it easier for toxins to enter the body.
Too much sugar can slow digestion. This leads to constipation and irregular bowel movements. Over time, the gut loses its ability to function well. This affects overall health and energy levels.
Sugar And Inflammation
High sugar intake triggers inflammation in the digestive tract. Inflammation causes redness, swelling, and pain. It can damage the intestines and other organs. Chronic inflammation may increase the risk of digestive diseases.
Inflammation also affects how the body fights infections. It can weaken the immune system in the gut. This makes it harder to stay healthy and recover from illness.
Addiction And Sugar Cravings
Eating too much sugar can create strong cravings. These cravings can feel like an addiction. People often want more sugar even after they know it is harmful. Understanding why sugar feels addictive helps control these urges. Learning ways to break the sugar habit supports better health.
Why Sugar Feels Addictive
Sugar triggers the brain to release dopamine. Dopamine is a chemical that makes you feel good. This feeling makes you want to eat sugar again and again. Over time, your brain needs more sugar to get the same pleasure. This cycle causes strong cravings and addiction-like behavior.
Sugar also affects the brain’s reward system. It can change how your brain reacts to food. This change can lead to eating more sugar than you want. The more sugar you eat, the harder it becomes to stop.
Breaking The Sugar Habit
Stopping sugar cravings takes time and effort. Start by reducing sugary foods slowly. Replacing sugar with healthy snacks helps control hunger. Drinking water can reduce the urge to eat sweets.
Eating balanced meals with protein and fiber keeps you full longer. This reduces the desire for sugar. Avoid buying sugary snacks to limit temptation. Finding other ways to feel good, like exercise, also helps break the habit.
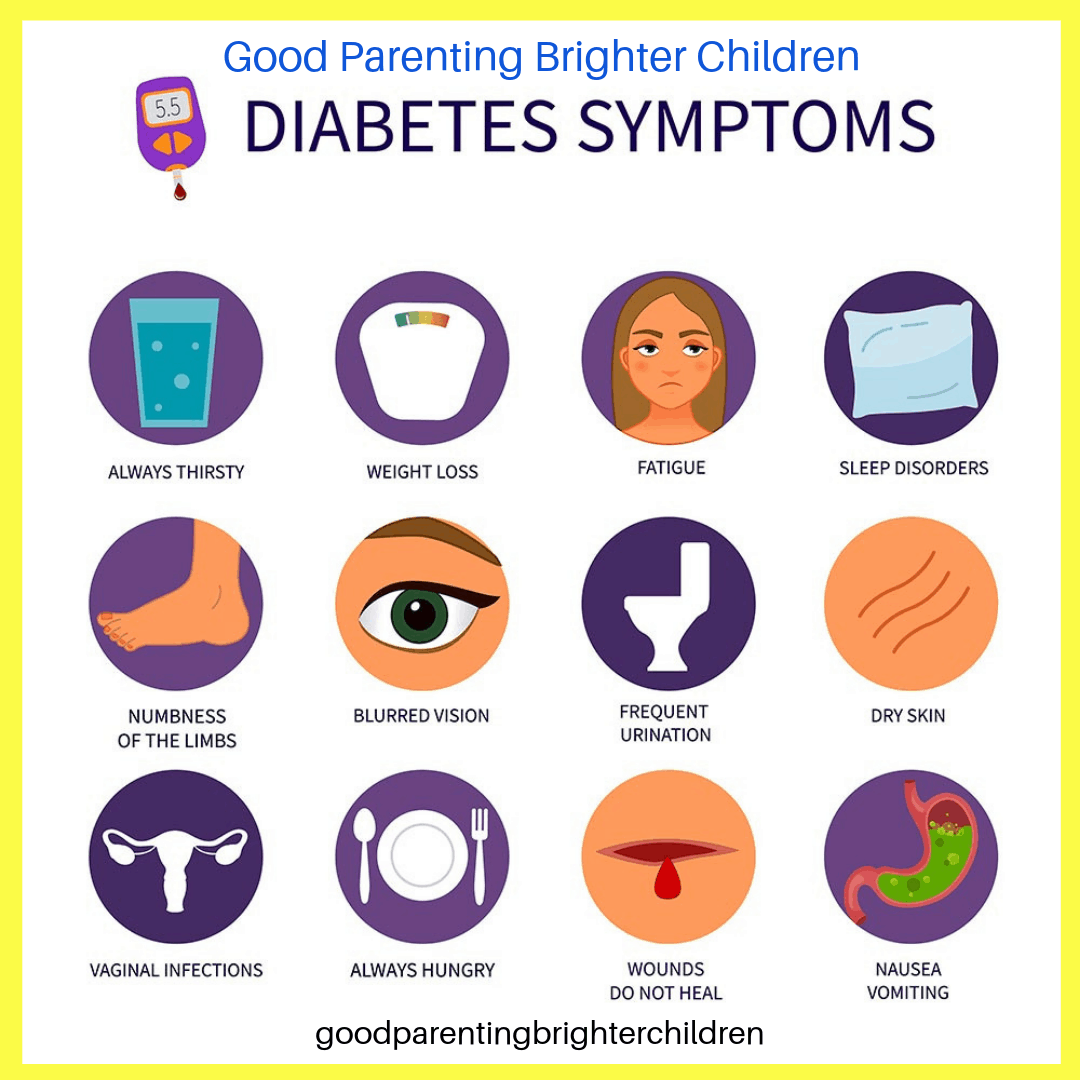
Credit: goodparentingbrighterchildren.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Common Side Effects Of Eating Too Much Sugar?
Eating too much sugar can cause weight gain, increased risk of diabetes, and tooth decay. It may also lead to fatigue and mood swings.
How Does Excess Sugar Affect Your Heart Health?
High sugar intake raises blood pressure and inflammation. This increases the risk of heart disease and stroke over time.
Can Eating Too Much Sugar Cause Skin Problems?
Yes, excess sugar can lead to acne and premature aging. It damages collagen, making skin less elastic and more prone to wrinkles.
Does Sugar Consumption Impact Mental Health?
High sugar intake can cause mood swings and increase anxiety. It may also contribute to depression by affecting brain function.
Conclusion
Eating too much sugar harms your body in many ways. It can cause weight gain and increase the risk of diseases. Your energy may crash after a sugar high. Teeth can get cavities and pain. Mood swings and tiredness often follow too much sugar.
Cutting back helps you feel better and stay healthy. Small changes make a big difference over time. Choose fresh fruits and water instead of sugary drinks. Your body will thank you for less sugar every day.
